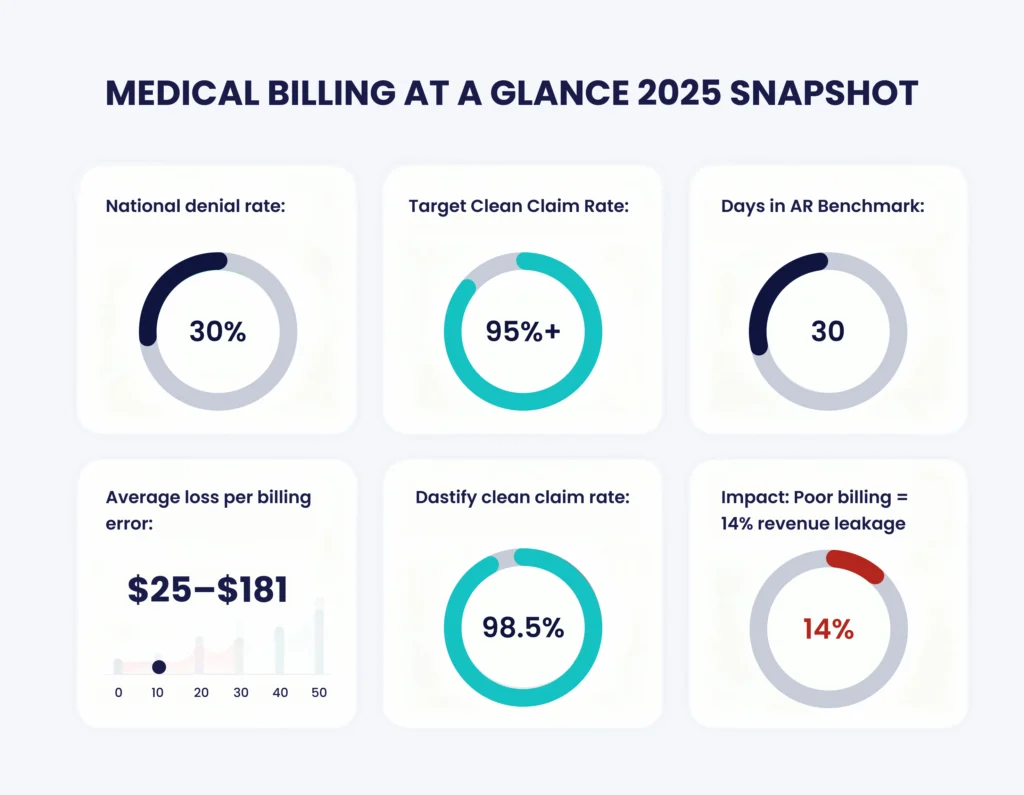
In 2025, nearly 41% of healthcare providers face denial rates of 10% or more, while almost 30% of all claims are denied or rejected on first submission. These challenges result in billions of dollars in lost revenue annually and place significant burdens on practice operations.
Medical billing is the essential process that translates patient care into timely, accurate reimbursements. It ensures compliance with complex regulations, secures fair payment for providers, and supports patients’ understanding of their financial responsibilities. Even though it underpins the entire healthcare delivery system, many physicians and practice managers lack formal training in billing operations.
This comprehensive guide covers:
- The basics and foundations of medical billing services
- Why billing is critical and increasingly complex
- What professional billing companies actually do
- How in-house, outsourced, and hybrid models compare
- The main benefits of different models of billing
- How to choose the right medical billing partner
Whether you are a physician ensuring proper reimbursement, a patient trying to understand your medical bills, or simply someone curious about how healthcare billing works, this blog will walk you through everything you need to know about Medical billing in 2025.
Basics of Medical Billing
Medical billing is the financial backbone of healthcare. It translates every diagnosis, test, or treatment into a financial transaction that ensures providers get paid, clinics stay operational, and patients understand what they are being charged for. Without an efficient billing system, healthcare organizations risk delayed reimbursements, cash flow gaps, and compliance issues.
This section lays out the core services, key terms, and step-by-step cycle.
What is Medical Billing?
Medical billing is the process of translating healthcare services into claims submitted to insurers and following up to ensure payment.
Each claim represents a patient’s visit, including their diagnosis, the care provided, and the procedures performed, all translated into standardized codes that insurers recognize.
Effective billing depends on a clear understanding of:
- ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems
- Payer-specific rules and documentation requirements
- HIPAA and CMS compliance standards
Even small errors can be costly. For example, coding Type 2 diabetes as Type 1 (E10.9 instead of E11.9) can result in a denial and delayed reimbursement. Accuracy and attention to detail ensure providers are paid in full and on time.
What Are Medical Billing Services?
A medical billing service handles the full end-to-end revenue cycle process: from patient registration, insurance verification, coding (e.g., ICD‑10/CPT/HCPCS codes), claim submission, payer follow-up, denial management, credentialing and enrollment payment posting, and payer enrolment.
When you are selecting an AI-powered medical billing service provider, you are effectively choosing who manages the bridge between clinical care and reimbursement in your practice.
The Core Components of Medical Billing Services
These functions form a sequential chain, each preventing downstream errors and ensuring the process flows without friction:
The core components of medical billing services are:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Insurance Verification | Confirms patient eligibility and benefits before appointments to prevent claim rejections. |
| Medical Coding | Converts diagnoses and procedures into standard codes (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS) to ensure payer compliance. |
| Charge Entry | Creates accurate charge sheets or superbills for each encounter. |
| Claim Submission | Submits clean claims electronically through clearinghouses to payers such as Aetna, Blue Cross Blue Shield, and UnitedHealthcare. |
| Payment Posting | Records payments from insurance and patients, reconciling discrepancies promptly. |
| Denial Management | Identifies, corrects, and resubmits denied claims to reduce lost revenue. |
| Accounts Receivable (A/R) Follow-Up | Monitors unpaid claims, ensures timely follow-up, and minimizes AR days. |
| Patient Billing | Sends clear, accurate statements to patients for balances due. |
These are the steps that create the basis for an efficient billing system to ensure claims are efficiently processed and providers are paid appropriately.

Key Terms and Concepts You Should Know
Fluency in these terms demystifies billing, enabling spot-checks on claims and audits. They’re the language of compliance and precision.
| Term | Purpose | Example | Why It Matters in Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICD-10 Codes | Identify diagnoses | E11.9 → Type 2 Diabetes | Ensures diagnostic accuracy for outcome-based reimbursements under value-based care models. |
| CPT Codes | Describe procedures | 99213 → Office visit | Directly influences payment amounts; updates annually, requiring vigilant training. |
| HCPCS Codes | Identify non-CPT services and supplies | J1885 → Ketorolac injection | Covers ancillary items like DME, preventing underbilling for comprehensive services. |
| CMS | Regulates reimbursement and claim standards | Medicare and Medicaid rules | Sets national benchmarks; non-adherence risks program exclusions or penalties. |
| EHR Systems | Store and link patient and billing data | Epic, Cerner | Integrates clinical and financial data, reducing manual entry errors by 50%+. |
| HIPAA | Ensures data privacy and compliance | Billing data protection | Mandates secure handling; breaches average $10M in costs, per HHS reports. |
These workflows vary by specialty. For example, behavioral health requires strict prior authorizations, cardiology involves high-complexity CPT coding, and orthopedics sees frequent modifier-driven denials. Specialty-specific billing expertise improves accuracy and reduces payer rejections.
Billing vs Coding
Coding and billing are intertwined, with errors in one rippling through the other. This section clarifies their roles and relationship, using comparisons to highlight why alignment is key to avoiding 22% of denials from coding mistakes.
How Are Medical Billing and Coding Connected?
Coding and billing are distinct but deeply linked. Coding translates clinical actions into standardized codes, while billing uses those codes to generate and submit claims.
| Aspect | Medical Coding | Medical Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts care into standardized codes | Converts codes into claims for payment |
| Goal | Clinical precision and compliance | Reimbursement and revenue management |
| Regulation | AAPC, AHIMA standards | CMS and HIPAA compliance |
| Error Impact | Wrong diagnosis or procedure code | Payment delays or denials |
Medical Billing vs Medical Coding
These terms are often used together but they are not the same thing. Here is a simple way to think about it. Coding converts the clinical note into standard codes. Billing takes those codes and turns them into claims, then follows up until the money is posted. If a coder assigns CPT 99213 for an office visit and ICD-10 E11.9 for Type 2 diabetes, the biller uses those codes to create the claim, submit it, and handle appeals if needed. An error at either step can slow or stop payment.
Medical Billing vs Coding Functions
| Function | Coding | Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Convert services into standardized codes | Create claims and track payment |
| Responsibility | Certified coders | Billers or billing specialists |
| Outcome | Accuracy in documentation | Timely reimbursement |
This comparison illustrates how coding lays the groundwork for billing success, emphasizing the need for cross-training to prevent silos and errors. In 2025, AI bridges this gap further by auto-flagging mismatches, but human oversight remains key for nuanced cases.
Revenue Cycle Management
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is the broader financial strategy that includes billing, collections, and compliance. It is often also referred to as the medical billing process or revenue cycle, and it starts with patient scheduling and ends when the final payment is posted. Each step is crucial for ensuring claim accuracy and prompt payment. This section explains its role and benchmarks, helping you measure and improve overall performance.
End-to-End Billing Process Explained
The billing cycle can be broken down into 8 key stages, which include:
| Stage | Description | Common Issue | Prevention Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Registration | Collect accurate demographic & insurance info | Missing or outdated info | Use automated forms in EHR for real-time validation. |
| Eligibility Verification | Confirm coverage & benefits | Denied claims due to ineligibility | Integrate payer APIs for instant checks at scheduling. |
| Coding & Charge Capture | Assign ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS codes | Coding errors or under coding | Employ AI-assisted tools for code suggestions. |
| Claim Submission | Send electronic claim to insurance | Incorrect format or missing NPI | Standardize templates with built-in scrubbers. |
| Adjudication | Insurance reviews and approves/denies | Missing documentation | Attach supporting notes proactively. |
| Payment Posting | Record received payments | Partial postings or errors | Automate reconciliation with bank feeds. |
| A/R Follow-Up | Track unpaid claims | Delayed Collections | Set automated alerts for aging thresholds. |
| Denial Management | Review & Resubmit denied claims | Ignored rejections cause revenue loss | Categorize denials for root-cause analysis. |
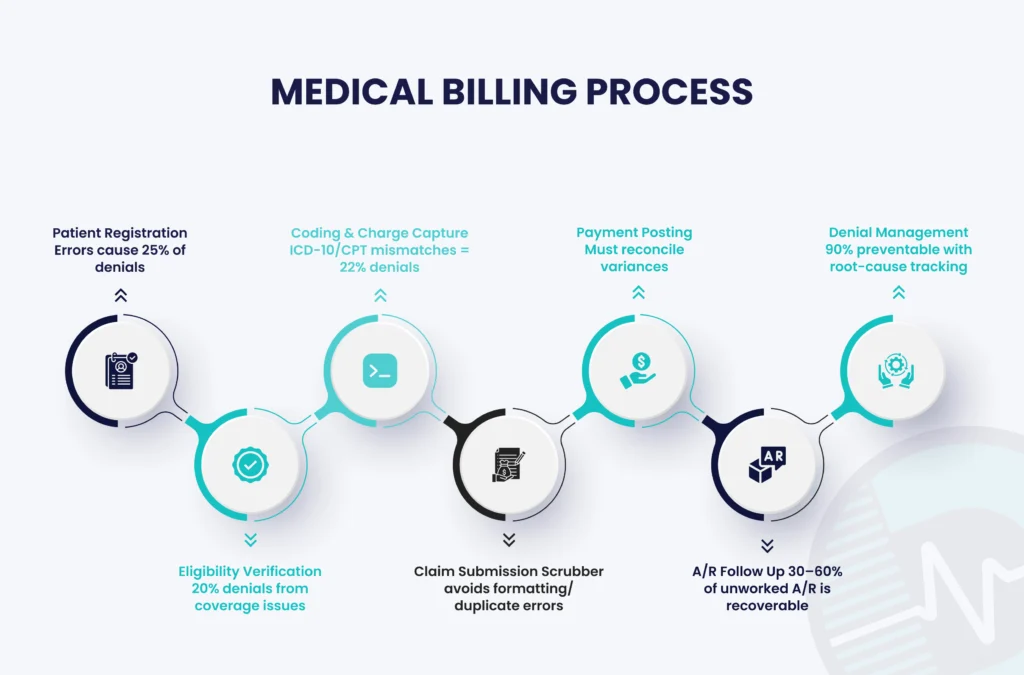
Claim Submission
Most claims pass through clearinghouses such as Availity, Change Healthcare, or Trizetto before reaching payers like Medicare, Medicaid, Blue Cross Blue Shield, Aetna, Cigna, or UnitedHealthcare. Ensuring proper formatting reduces rejections at the clearinghouse level.
The medical billing process, often called the revenue cycle, is a multi-step journey that starts before the patient sees the doctor and ends long after they have left. Each step is crucial for ensuring claim accuracy and prompt payment, with front-end investments yielding the highest ROI.
Average Time Spent per Step
Each phase in the billing process takes time, and even small delays can slow down payments. Knowing how long each step usually takes helps a practice see where things get stuck and where improvements will have the biggest impact.
| Billing Step | Avg. Time Required |
|---|---|
| Pre-Authorization | 5–15 minutes per patient |
| Registration & Verification | 5–10 minutes |
| Coding & Charge Capture | 10–20 minutes |
| Claim Submission | 1–2 minutes |
| Payer Adjudication | 15–30 days |
| Payment Posting | 3–5 minutes |
| A/R Follow-Up | Weekly–monthly |
| Denial Management | 24–48 hours per claim |
| Patient Billing | 5–10 minutes per account |
Key Benchmarks
Tracking these metrics provides a health check for your RCM, revealing strengths and areas for improvement. Regular audits against these benchmarks, ideally monthly, guide strategic decisions, such as investing in staff training or software upgrades, and correlate strongly with overall profitability.
| Metric | Definition | Healthy Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Clean Claim Rate | Claims accepted without edits | 95% or higher |
| Days in Accounts Receivable | Average days until payment | 30 days or less |
| Net Collection Rate | Collected revenue vs allowed charges | 96% or higher |
| Denial Rate | Percentage of denied claims | 5% or less |
Practices exceeding these benchmarks often report 15-20% higher profitability, demonstrating the tangible ROI of robust RCM. Use them as guardrails to benchmark against peers via tools like MGMA surveys.
Common Challenges
Challenges like denials and manual errors are universal, but they’re largely preventable. This section outlines the top obstacles, their impacts, and actionable fixes, drawing on industry data to help you prioritize.
Most Frequent Obstacles in Medical Billing
Medical billing isn’t without its challenges. Providers frequently encounter problems that can hinder the revenue cycle and their bottom line. The following are some of the most frequent roadblocks:
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| High Denial Rates | Lost revenue & delayed payments | Track denials and analyze the reasons to fix issues before they grow. |
| Manual Workflows | Slow and prone to errors | Automate tasks to speed up processes and reduce mistakes. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Compliance risks | Keep your team trained and perform regular audits to stay on track. |
| Staff Shortages | Slow follow-up on claims | Outsource or use automation to fill in the gaps. |
| Value-Based Payments | Complex reimbursement systems | Train your team and optimize your process to handle these changes. |
Solving these problems is crucial for improving the efficiency and financial stability of your practice. Addressing them early can make all the difference.
Key Challenges in Medical Billing
For every denied claim and delayed payment, the financial impact of billing inefficiencies reaches farther than just numbers: it equates to operational bottlenecks, overworked staff, and time lost that directly affects patient care and revenue flow. To understand where these inefficiencies begin, it helps to look at the most common challenges that disrupt billing operations.
| Challenge | Operational Impact | Effective Solution |
|---|---|---|
| High Denial Rates | Each denied claim requires rework, slowing down payments and increasing administrative costs. | Automate claim scrubbing and track denial trends to address recurring issues. |
| Staff Turnover | High turnover disrupts workflows and increases training costs, leading to inconsistency in claim handling. | Standardize processes and use automation to reduce dependency on manual tasks. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Frequent updates to HIPAA and CMS guidelines make compliance management difficult. | Conduct quarterly audits and staff training to stay aligned with regulations. |
| Manual Workflows | Paper-based or fragmented systems increase error rates and slow reimbursement cycles. | Integrate EHR and RCM tools for faster, more accurate data transfer. |
| Evolving Payer Requirements | Constant changes in payer policies lead to confusion and inconsistent reimbursement. | Use payer portals and automated eligibility verification for real-time updates. |
Each of these challenges feeds into the next, creating a cycle of inefficiency that is difficult to break without structural improvement. Among them, one issue stands out as both the most frequent and the most preventable: claim denials.
Clinic with 8 providers, 12% denial → after structured RCM + automation → 4% denial, AR 55 → 32 days.”
Most Common Reasons for Claim Denials
Claim denials are often symptoms of deeper systemic issues, not just isolated mistakes. Most arise from small, fixable errors that multiply over time, causing revenue leaks that go unnoticed until they accumulate.
According to MGMA, up to 90% of denials are preventable through better front-end verification, coding accuracy, and real-time claim tracking. Understanding the leading causes helps providers take proactive action.
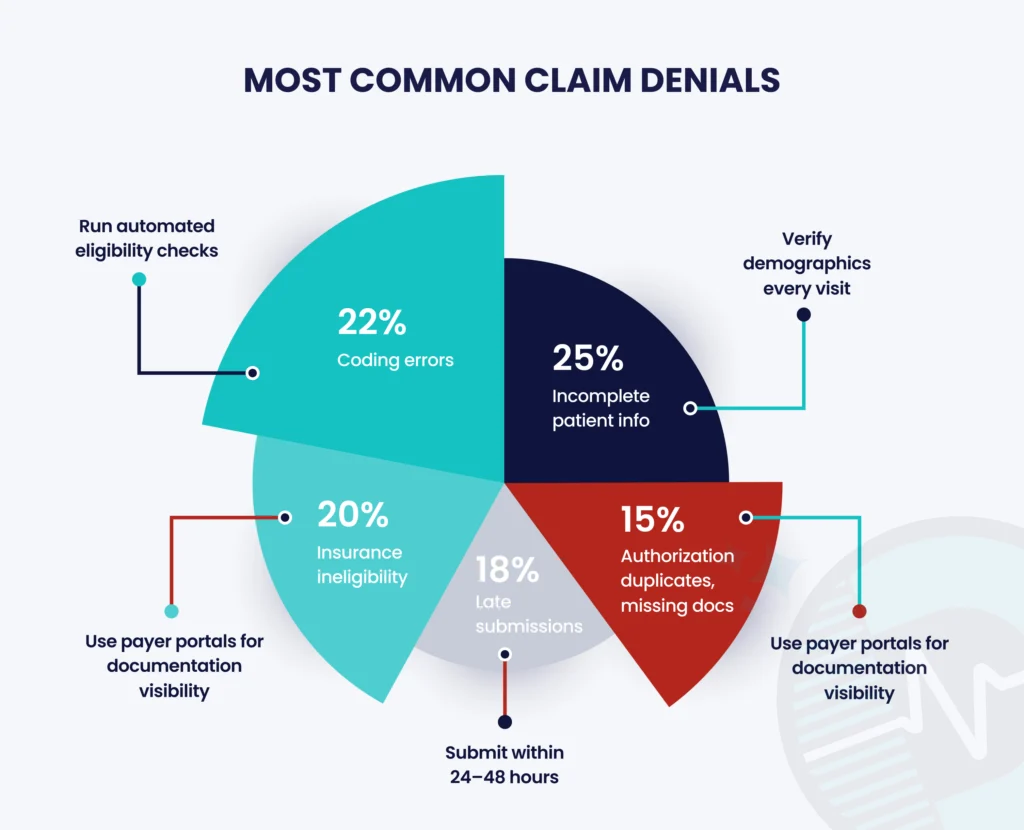
| Reason for Denial | Estimated Share | How to Prevent It |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete patient information | 25% | Verify demographics and insurance details before each visit. |
| Coding errors | 22% | Conduct regular coding audits and ensure staff stay updated on ICD-10 and CPT revisions. |
| Insurance ineligibility | 20% | Use automated eligibility verification tools to confirm coverage at scheduling. |
| Late submission | 18% | Configure RCM software to flag claims approaching submission deadlines. |
| Other causes (authorization, duplicates, etc.) | 15% | Implement claim tracking dashboards for early error detection. |
Most claim denials start with front-end errors. Fixing the first few minutes of your billing workflow can save weeks of downstream rework.
Addressing these issues at the front end of the billing process is far more cost-effective than resolving them later. While no system can eliminate denials entirely, the right mix of automation, process design, and expert oversight like the approach used by Dastify Solutions, can significantly reduce their frequency and financial impact.
The Cost of Inefficient Billing
Every claim error, missing document, or late submission chips away at a healthcare provider’s revenue. Billing inefficiencies are not just administrative setbacks; they directly affect profitability, compliance risk, and cash flow stability.
| Metric | Industry Insight | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Average Claim Denial Rate | Roughly 30% of medical claims are denied or rejected on their first submission, representing billions in lost revenue each year. | MGMA |
| Claim Rework Cost Per Denial | Each denied claim costs an average of $25 to correct and resubmit, not including lost staff time or delayed reimbursements. | Change Healthcare 2023 Revenue Cycle Denials Index |
| Administrative Cost of Billing | Billing-related tasks consume up to 14% of a physician’s total revenue, mostly due to manual entry and repetitive processes. | JAMA |
| HIPAA Violation Fines | Non-compliance penalties can range from $100 to $50,000 per incident, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million. | HHS.gov |
| Impact of Outsourcing Billing | Practices that outsource to certified billing specialists see collection rates improve by 15–20% and denial rates drop by nearly half. | AAPC |
| Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R) | Industry benchmarks suggest that efficient billing systems maintain A/R below 40 days, while poorly managed systems average 60–90 days. | HFMA |
Collectively, these figures show that billing inefficiency is not just about mistakes; it is about missed opportunities for revenue growth and long-term financial stability.
Medical Billing Models
Selecting the right model depends on your practice’s size and goals. This section compares the three main approaches, incorporating manual vs. automated differences, to help you weigh trade-offs for efficiency and scalability.
Types of Medical Billing Services
Practices can choose among three main models for managing their billing operations. The best fit depends on the practice’s size, specialty, and financial goals.
| Feature | In-House Billing | Outsourced Billing | Hybrid Billing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Staff and processes are fully managed internally | Managed by external experts via a service agreement | Shared control. Internal team handles front-end; experts handle backend |
| Cost | High fixed costs from salaries, software, and training | Variable fee, often a percentage of collections | Moderate blend of fixed and variable costs |
| Expertise | Limited to knowledge of the in-house team | Access to certified specialists familiar with payer rules | Leverages both internal and external knowledge |
| Scalability | Difficult and expensive to scale | Scales quickly with practice volume | Moderately scalable |
| Technology | Requires investment and ongoing maintenance | Advanced software and analytics included | Mix of internal and vendor-provided tools |
| Best For | Large practices with dedicated resources | Practices seeking efficiency and cost reduction | Organizations wanting a tailored approach |
The Difference Between Manual and Automated Billing
When choosing a billing method, it’s important to understand how manual billing differs from automated workflows. Each method impacts your practice’s accuracy, speed, cost, and compliance in different ways. By comparing the two, healthcare providers can make better decisions on which method suits their needs.
| Feature | Manual Billing | Automated Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Error Rate | High (up to 15–20%) | Low (<5%) |
| Speed | Slow (days to weeks) | Fast (hours to days) |
| Staff Requirement | Larger team needed | Fewer staff required |
| Compliance | Prone to human error | Built-in checks for HIPAA/CMS |
| Reporting | Limited analytics | Real-time dashboards & KPIs |
Practices that switch to automated billing often see 30% faster reimbursement and reduced claim denials.
In-House vs Outsourced Medical Billing
Before choosing a vendor, take time to decide whether your practice should manage billing internally or outsource it to a professional medical billing company. Both approaches can work, but each has distinct strengths and trade-offs.
| Feature | In-House Billing | Outsourced Medical Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over daily operations and staff | Shared control, external specialists manage the process |
| Initial Investment | High, including salaries, training, and software | Lower upfront costs since vendors already have infrastructure |
| Scalability | Limited by available staff and time | Easily scales with your growth or added specialties |
| Access to Technology | Requires ongoing investment | Vendors typically use advanced automation and analytics tools |
| Compliance Responsibility | Fully on your practice | Vendor assumes part of the compliance responsibility |
| Cost Model | Fixed overhead | Usually a percentage of collections or per-claim fee |
| Best For | Large, stable practices with strong internal teams | Growing or cost-conscious practices that value efficiency |
According to MGMA 2024 data, practices outsourcing billing achieve an average 94.8 % net collection rate versus 89.6 % for in-house operations (source: MGMA Cost and Revenue Survey).
Should You Outsource Your Billing or Keep It In-House?
Deciding whether to manage billing in-house or outsource to a third-party company is a key decision for healthcare providers. The best choice often depends on factors like practice size, available staff, technology infrastructure, and financial objectives. To help you make an informed decision, here’s a side-by-side comparison of the advantages and drawbacks of each option.
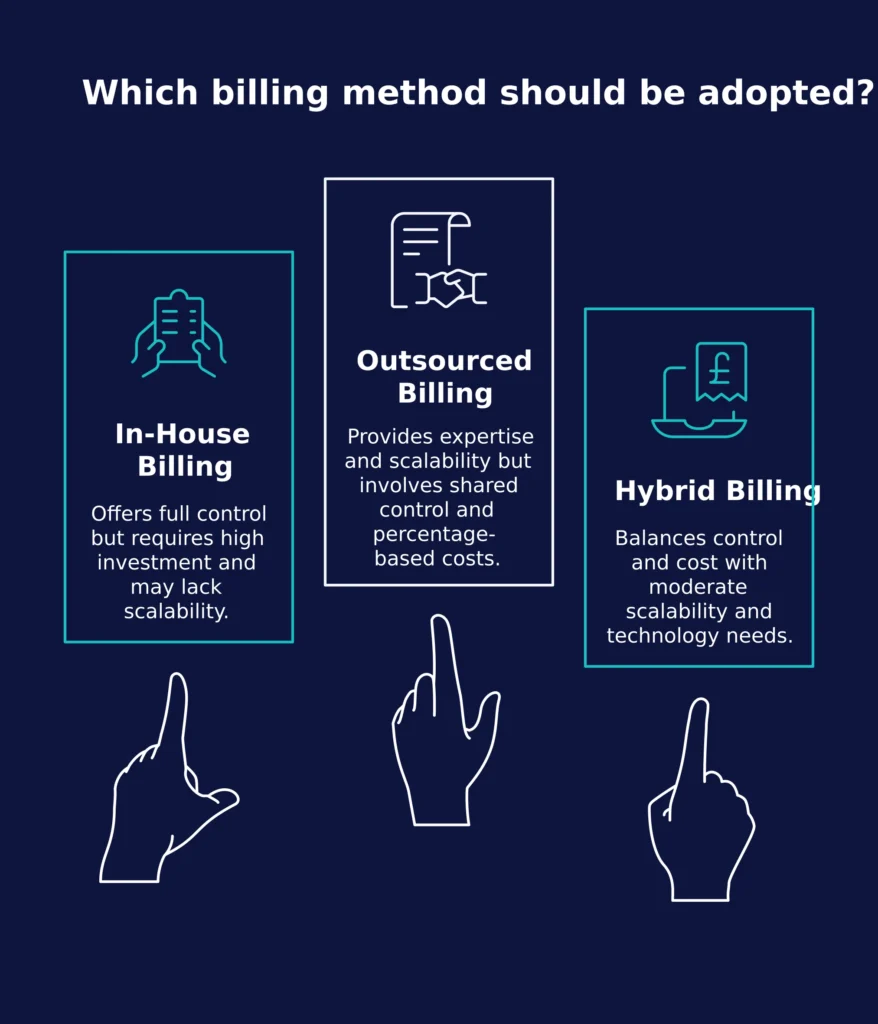
| Criteria | In-House Billing | Outsourced Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Fixed overhead (staff, software) | Variable cost per claim or collection |
| Expertise | Requires ongoing staff training | Access to certified billing professionals |
| Scalability | Limited by internal resources | Easily scales with practice growth |
| Technology | Needs internal EHR/RCM setup | Vendor provides advanced systems |
| Compliance | Internal responsibility | Vendor ensures HIPAA and CMS compliance |
By comparing these two approaches, you can identify which one best aligns with your practice’s goals, helping you maintain efficient revenue cycles while focusing on patient care.
How To Decide Whether to Outsource Medical Billing or Keep It In-House?
Ask yourself these key questions before deciding to manage medical billing internally or partner with an outsourcing medical billing company:
- Do you have trained billing staff who can manage coding, claim submission, denial management, and payer rules effectively?
- Are your first-pass clean claim rate and days in A/R within acceptable limits?
- Can you keep pace with technology updates, compliance changes, and payer policy revisions?
- Is your practice growing or adding new specialties that will make billing more complex?
- Would outsourcing reduce overall costs or improve revenue performance compared to keeping billing in-house?
If you’re unsure about these answers or struggling with claim accuracy, rising denials, or cash flow delays, outsourcing may be the more practical and scalable choice.
| Ready to analyze your revenue leaks? Request a free Denial Audit from Dastify Solutions and get a breakdown of preventable losses within 48 hours. |
Why Outsourcing is Better
Outsourcing isn’t just a cost-saver, it’s a strategic move for reliability and growth. This section highlights the advantages, backed by metrics, to show how it addresses common pain points.

Real-World Results ( Case Improvements)
- A 12-provider behavioral health clinic in California reduced denial rates from 18% to 5% within 90 days by implementing structured denial analytics and payer-specific workflows.
- A cardiology group in Texas cut AR days from 57 to 29 after adding automated eligibility verification and monthly coding audits.
- A multi-location orthopedic practice improved net collections by 22% after outsourcing to a certified billing team and replacing manual workflows with automated claim scrubbing.
Why Outsourcing Medical Billing
Every healthcare practice invests time and money to get paid for the care it provides. But when billing is managed entirely in-house, that investment often grows faster than the return. Salaries, software subscriptions, ongoing coder training, compliance audits, and IT maintenance add up quickly. Meanwhile, the workload never stays constant. Claim volumes fluctuate, denials rise and fall, payer rules change, and staff availability varies.
Outsourcing changes the equation. Instead of carrying fixed costs, you pay for measurable performance. External billing specialists already have certified teams, advanced RCM software, and established compliance systems. You access all of that instantly, without having to build or maintain it yourself. Moreover, according to the Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA), healthcare organizations that outsource billing cut operational costs by up to 30% and shorten reimbursement cycles by 20–40%.
| Metric | In-House Billing | Outsourced Billing |
|---|---|---|
| First-pass claim rate | 80% | 95% |
| Average days in A/R | 45 | 30 |
| Cost as % of collections | 10–12% | 6–8% |
| Staff time on billing tasks | About 30% of admin hours | Less than 10% |
Choosing the Right Partner
Choosing a partner is about alignment, not just price. This section guides you through evaluation criteria, metrics to monitor, and contract tips for a successful partnership.
What to Look for in a Medical Billing Service Provider
Once you decide to outsource, evaluate potential partners carefully. The right billing provider will align with your specialty, technology environment, and compliance expectations.
Experience and Specialization
- Choose a company experienced in your medical specialty.
- Request metrics: clean claim rate, average AR days, and denial rate.
- Top performers maintain 95%+ first-pass acceptance and <5% denial rate.
- Ask for references and measurable case studies.
Compliance and Data Security
- Confirm HIPAA compliance and strong data protection protocols.
- Ensure staff are certified coders familiar with ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS updates.
- Ask about encryption, data backups, and internal audits.
Technology and Integration
- Verify compatibility with your EHR system (Epic, Cerner, Athenahealth, etc.).
- Look for automation tools, AI-assisted claim scrubbing, and real-time dashboards.
Transparency and Reporting
- Expect clear reports showing clean claim rates, AR trends, and denial causes.
- Insist on access to a secure client dashboard.
- Schedule regular review meetings to track results.
Cost and Contract Flexibility
- Most vendors charge 3–9% of monthly collections or a flat per-claim rate.
- Confirm what’s included (credentialing, reporting, analytics) and what’s extra.
- Value transparency and reliability over the lowest price.
- Before signing, request HIPAA audit logs and ask for proof of SOC-2 Type II certification a standard Dastify Solutions maintains annually.
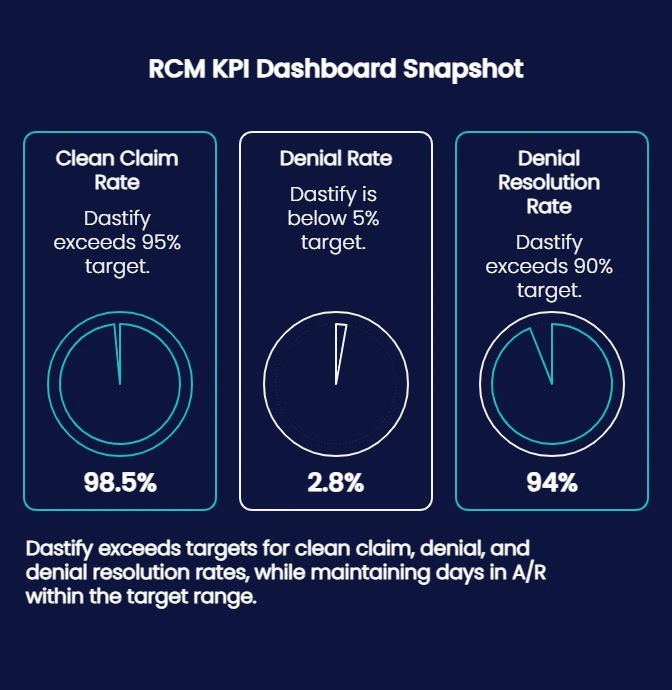
Performance Metrics to Monitor
After selecting a billing service, consistent performance monitoring ensures your vendor continues to deliver results. These metrics reflect the health of your revenue cycle.
| KPI | Definition | Ideal Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| First-Pass Clean Claim Rate | Percentage of claims accepted on first submission | 95% or higher |
| Average Days in Accounts Receivable (AR) | Average time from claim submission to payment | 30–35 days |
| Denial Rate | Percentage of claims denied by payers | Under 5% |
| Denial Resolution Rate | Percentage of denied claims successfully corrected and paid | Over 90% |
| Turnaround Time | Average time from service date to claim submission | 7–14 days |
| Cost to Collect | Cost of collecting each dollar of revenue | 5–7% |
Across Dastify Solutions’ clients, first-pass acceptance consistently exceeds 98 %, with average A/R days of 31 numbers verified through quarterly audits.
Cost Considerations and Hidden Factors
When comparing in-house billing with outsourcing, focus on total cost of ownership, not just vendor fees. The true cost includes technology, labor, and the price of inefficiency. Understanding the True Cost
- Vendor pricing: Most medical billing companies charge 3–9% of collections or a per-claim fee.
- In-house cost: Salaries, training, software, and turnover often make internal billing more expensive than expected.
- Hidden costs: Look for setup fees, software migrations, or penalties for early termination.
| Cost Component | In-House Billing | Outsourced Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Up-Front Setup | High; hardware and hiring | Low: vendor handles setup |
| Ongoing Overhead | Staff and training costs | Vendor fee with minimal extras |
| Cost per Dollar Collected | Often higher | Typically lower with automation |
| Scalability | Limited by staff | Flexible with volume |
| Risk of Errors/Denials | Higher without automation | Lower with experienced vendor |
Before finalizing a contract, request a full breakdown of costs and calculate ROI. For example, reducing your denial rate from 8% to 4% and cutting AR days from 50 to 35 can create a substantial cash flow gain.
Contract Terms and Ongoing Support
Before signing, carefully review:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Targets for claim submission and AR timelines.
- Exit Clauses: Ensure easy, secure transition if you switch vendors.
- Scalability: Confirm capacity for future growth or additional locations.
- Dedicated Support: Expect responsive communication and a named account manager.
Join providers who trust Dastify Solutions for 95%+ clean claims, faster payments, and real financial results.
Final Checklist: Before You Decide
Use this quick list to compare and narrow down your options: o Proven experience in your specialty o HIPAA and CMS compliance o Seamless EHR integration o Transparent pricing and contracts o Regular reporting and performance reviews o Dedicated support and scalability
Ready to see your own KPIs improve? Schedule a Free RCM Audit and see how Dastify Solutions can increase collections by up to 20 % within 90 days.
Who Should Consider Outsourcing Billing?
- Outsourcing is generally a better fit for practices with:
- 1–15 providers
- High denial rates (10%+)
- AR days above 40
- Rapid growth or new locations
- Limited internal billing staff
- Specialty-specific billing needs (e.g., behavioral health, cardiology, pain management)
Larger groups (20+ providers) often use hybrid models combining internal oversight with external expertise for scalability.
Future Billing Trends
The landscape is evolving rapidly with AI and telehealth. This section outlines key trends, so you can prepare your practice for smarter, more connected billing.
The Future of Medical Billing
Medical billing is entering a smarter, more connected stage. The focus is shifting from routine claim processing to systems that predict issues early, keep providers informed, and give patients clearer insight into their costs.
- Predictive Tools That Prevent Errors Modern billing platforms can now spot likely denials before a claim is sent. By analyzing past data and payer behavior, they help staff correct problems early. Studies from CAQH show that automation and predictive tools could save U.S. providers more than $16 billion a year by reducing rework and manual follow-ups.
- Clear, Real-Time Reporting Instead of waiting weeks for claim updates, practices are beginning to use dashboards that show revenue flow and claim status in real time. This visibility allows administrators to act quickly, track performance, and plan resources with confidence.
- A Better Patient Experience Patients now expect clarity. Digital billing portals, upfront cost estimates, and easier payment options are becoming standard. These tools build trust and reduce confusion about what patients owe and why.
- Connected and Cloud-Based Systems Cloud billing platforms are replacing disconnected software. When billing tools work directly with electronic health records, information moves smoothly from visit to payment, cutting down on errors and delays.
- Smarter Compliance Frequent updates from CMS and private payers make manual rule tracking impossible. Modern systems handle those updates automatically, helping practices stay compliant and avoid costly mistakes.
Trends in Healthcare Billing Solutions in 2025
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, so does the way billing is handled. Some key trends include:
- Automation & AI: Automating the billing process helps predict and prevent denials, improving efficiency.
- Cloud-Based Software: Gives real-time access to billing data and enhances security.
- Telehealth Billing: With the rise of virtual care, new codes and models are required for accurate billing.
- Patient Financial Engagement: Clearer statements, cost estimators, and easier online payment options improve patient satisfaction.
- Data Analytics: Real-time dashboards and reporting platforms provide providers with a better understanding of their financial performance.
What Trends Are Shaping the Future of Medical Billing?
| Trend | What It Means | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Driven RCM | Automates claim scrubbing and denial prediction | 30% faster reimbursements |
| Value-Based Care | Payment tied to patient outcomes | Requires advanced data reporting |
| Telehealth Billing | New codes and payer requirements | Expanding need for compliance updates |
| Patient Financial Engagement | Clear, digital-first communication | Higher collection rates and satisfaction |
| Data Analytics in RCM | Real-time dashboards for performance | Improved transparency and forecasting |
Frequent updates from CMS and private payers make manual rule tracking impossible. Modern systems handle those updates automatically, helping practices stay compliant and avoid costly mistakes. When billing tools work directly with electronic health records, information moves smoothly from visit to payment, cutting down on errors and delays. These integrations future-proof operations against regulatory shifts and technological advancements, with 70% of practices planning AI pilots by year-end per HFMA surveys.
| Want to compare in-house vs outsourced costs for your practice? Book a Free RCM Cost Analysis and see the savings potential. |
Best Practices for Providers
Implementing proven habits can yield quick wins. This final section 9 offers a checklist and strategies, tying everything together for continuous improvement.
Medical Billing Best Practices for Providers
1. Verify Early, Bill Right
Perform eligibility and prior authorization checks before service delivery. Most denials stem from missing or outdated insurance information.
2. Train for Coding Accuracy
Offer quarterly workshops on ICD-10 and CPT updates. Even a 1% increase in coding precision can improve reimbursement by 5–8%.
3. Use Technology for Efficiency
Automation and AI tools can reduce claim denials by up to 30%, according to 2025 RCM benchmarks.
4. Monitor Key Metrics
Set monthly targets for Clean Claim Rate, A/R days, and Denial Rate. Visualize data using dashboards in your EHR.
5. Enhance Patient Engagement
Offer online payment portals, cost estimators, and clear bills to increase collection rates and satisfaction.
Monthly Targets and Strategies for Continuous Improvement
Set monthly targets for Clean Claim Rate, A/R days, and Denial Rate. Visualize data using dashboards in your EHR. Offer quarterly workshops on ICD-10 and CPT updates. Even a 1% increase in coding precision can improve reimbursement by 5–8%. Automation and AI tools can reduce claim denials by up to 30%, according to 2025 RCM benchmarks. Strategies like peer audits and cross-departmental reviews promote a culture of excellence, yielding compounding benefits over time, e.g., a 6-month pilot could lift net collections 12%. Review progress in team huddles, adjusting based on trend data for adaptive excellence.
Conclusion:
You’ve now got a complete roadmap to medical billing: from foundational terms and processes to overcoming challenges, choosing models, and embracing future trends. Whether you optimize in-house, outsource for efficiency, or adopt AI-driven tools, the goal is the same: faster payments, fewer denials, and more time for patient care. Remember, efficient billing isn’t just about revenue; it’s about sustainability and trust in your practice.
Take the first step today. Schedule a free RCM audit with Dastify Solutions to uncover hidden opportunities and boost collections by up to 20% in 90 days.


