Introduction: When Claim Denials Drain Your Practice
For many healthcare practices, denied claims and prolonged A/R cycles are silent profit killers. They lead to unpredictable revenue, staff burnout, and operational burden. According to HFMA, 22% of healthcare leaders report losing at least $500,000 annually to denials, while 1 in 10 loses over $2 million each year.
If you’re looking to understand why denials occur, how they affect your revenue, and what steps you can take to fix them, you’re in the right place. In this blog, we’ll uncover how an efficient denial management workflow can reclaim lost revenue, prevent repeat errors, and strengthen your RCM process.
To ensure clarity, this guide follows a structured approach: why denials happen, how to fix them, and how to prevent them permanently.
What is Denial Management in Medical Billing?
Denial management is a core component of Revenue Cycle Management (RCM). It identifies, corrects, and prevents claim denials, ensuring accurate billing and consistent cash flow.
How Denial Management Protects Revenue
Every denied claim delays payment and increases administrative burden. Nearly 1 in 5 in-network claims were dismissed in 2023, costing the U.S. healthcare industry billions in lost reimbursements. (KFF). The national average denial rate sits around 11%, while best-performing practices maintain <5% this creates a major performance gap that denial management closes.
Denial Management Protects Revenue in Several Key Ways:
Nearly 1 in 5 in-network claims were denied in 2023, according to KFF, leading to billions in lost reimbursements. Denial management directly addresses these revenue leaks by:
- Capturing Lost Revenue: Up to 65% of denied claims are never resubmitted due to administrative backlog, unclear responsibilities, or short payer deadlines. A structured workflow ensures every claim is corrected and resubmitted.
- Reducing Rework Costs: Denied claims cost $25–$50 each to reprocess. Addressing the root causes reduces repeated errors and saves time and money.
- Accelerating AR Recovery: Faster resubmissions and aggressive follow-ups trigger immediate AR recovery, turning aged claims into liquid cash and improving your overall collection ratio.
- Preventing Recurring Denials: Identifying patterns in coding, eligibility, or documentation prevents future denials.
- Optimizing Staff Time: Automation and clear workflows allow staff to focus on high-value activities rather than repetitive follow-ups.
In short: Denial Management is Not Reactive Work, It’s Revenue Protection.
Stop leaving money on the table and recover the revenue you already earned.
Common Causes of Denials
Understanding “why” claims are denied is the first step toward eliminating revenue loss. According to Change Healthcare, the national average denial rate is 11%, with 80–90% of them preventable.
1. Incomplete or Incorrect Information
Errors in patient demographics, insurance ID, or claim coding remain top denial triggers. Even small mistakes, like a misspelled name or a missing modifier, can lead to rejections.
2. Eligibility and Coverage Issues
Submitting claims for patients who aren’t eligible or whose insurance plans have expired leads to instant denials. Verifying eligibility upfront can eliminate a large share of these preventable errors.
3. Lack of Prior Authorization
Many payers require pre-authorization for specific procedures or medications. Missing these approvals can lead to claim denials, even if the service was medically necessary.
4. Out-of-Network Services
Claims for services provided outside the patient’s insurance network are often denied or reimbursed at lower rates. Clear communication with patients about their network status can reduce disputes and denials.
5. Duplicate Claims
Submitting the same claim multiple times (intentionally or accidentally) can flag it as a duplicate and lead to denial. Automation tools can help detect and prevent duplicate submissions.

6. Medical Necessity Denials
When documentation doesn’t clearly support the need for a service or test, payers may classify it as not medically necessary. Detailed clinical documentation helps justify treatment decisions.
7. Coding Errors
Incorrect or outdated CPT, ICD-10, or HCPCS codes are among the most frequent causes of denials. Continuous coder training and audits are essential to avoid costly mistakes.
8. Timely Filing Limits
Each payer has strict deadlines for claim submission. Missing these timelines results in automatic denials that are rarely reversible.
9. Bundling and Unbundling Errors
Submitting multiple claims for procedures that should be billed together, or failing to bundle them correctly can trigger payer rejections.
10. Coordination of Benefits (COB) Issues
When a patient has multiple insurance plans, confusion about which payer is primary often causes denials. Proper verification at registration can prevent COB-related issues.
These causes align with national denial benchmarks and should be tracked monthly in every practice.
| Cause of Denial | Estimated % of Total Denials | Source |
| Miscoded or incomplete claims | 34% | Change Healthcare Denials Index 2022 |
| Eligibility/administrative issues | 18% | Change Healthcare Denials Index 2022 |
| Excluded or non-covered services | 16% | Change Healthcare Denials Index 2022 |
| Missing prior authorization/referral | 9% | HFMA |
| Lack of medical necessity | 6% | AHA |
Most of these denials are front-end preventable before the claim even reaches a payer.
Types of Denials
| Hard Denials: | Soft Denials |
| Non-payable and typically require appeals, often tied to medical necessity or preventable coding/documentation errors. | Temporary and reversible; usually administrative issues that can be corrected and resubmitted. |
Knowing the difference allows teams to prioritize high-impact recoverable claims.
The Denial Management Workflow: A Step-by-Step Approach
A strong denial management workflow ensures every denied claim is identified, tracked, corrected, and prevented from recurring. Below is a breakdown of an effective workflow that medical billing companies use to minimize denials and improve A/R performance.
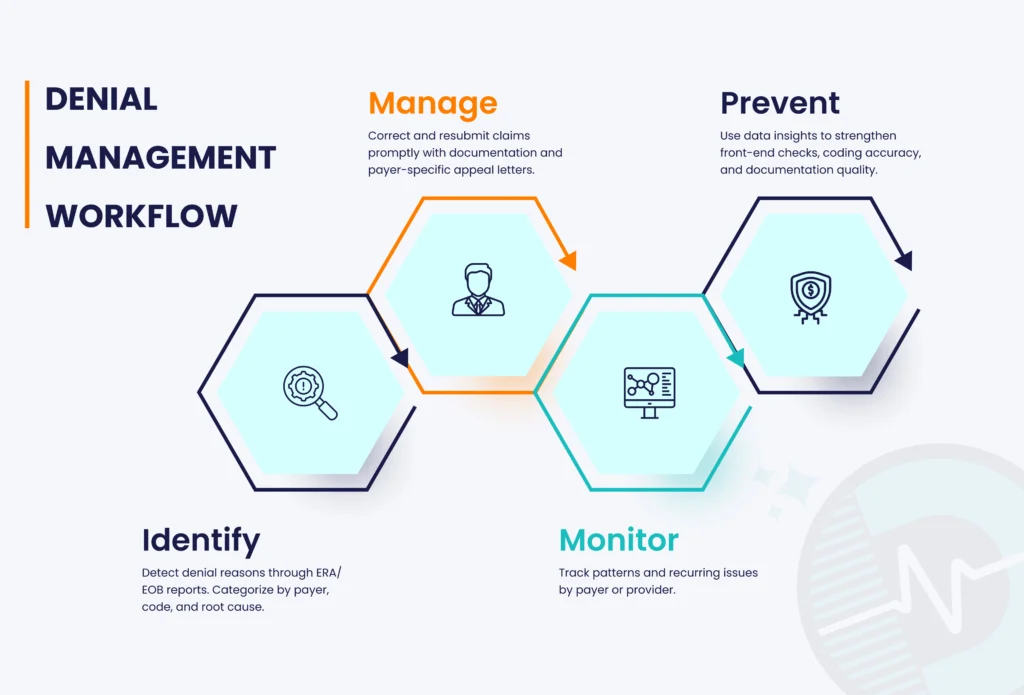
- Identify – Detect denial reasons through ERA/EOB reports. Categorize by payer, code, and root cause.
- Manage – Correct and resubmit claims promptly with documentation and payer-specific appeal letters.
- Monitor – Track patterns and recurring issues by payer or provider.
- Prevent – Use data insights to strengthen front-end checks, coding accuracy, and documentation quality.
The solution? Outsourcing denial management services ensures these steps are executed efficiently by experts using automation and analytics.
In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Claim Denials
Not all denials are operational mistakes; many are tied to contractual or network-related limitations.
| In-Network Denials | Out-of-Network Denials |
|---|---|
| Caused by: Missing authorization Invalid eligibility Non-covered benefits Late filing Why it matters: In-network claims offer better reimbursement, but internal workflow gaps can still cause unnecessary denials. | Common when: Plan excludes OON benefits Payer applies carve-outs Procedure is flagged “non-emergent” Why it matters: These denials can significantly delay or eliminate reimbursement unless patients are clearly informed upfront. |
Upfront patient communication is critical to reduce OON disputes.
Which Payers Deny the Most Claims?
Which type of payer denies the most claims? A 2023 analysis by KFF found that people covered by private payers were more likely to have denied claims than those covered by public payers.
KFF 2023 Data:
- Employer-sponsored insurance: 21% denial rate
- Marketplace plans: 20%
- Medicaid: 12%
- Medicare: 10%
| This is why payer-specific denial workflows are non-negotiable. |
Top Denial Codes (CARC/RARC) Every Provider Must Track
These codes appear in >70% of provider denials nationwide:
- CO-16 – Missing information
- CO-22 – Payment adjusted, contractual obligations
- CO-109 – Claim/service not covered
- PR-1 – Deductible amount
- PR-204 – Service not covered under patient’s plan
- CO-50 – Non-covered services
Tracking these alone reduces preventable denials by 25–40%.
Proven Strategies to Prevent Denials
According to AHIMA research, leading healthcare organizations focus on prevention and leverage data-driven insights rather than reactive strategies.
Key strategies include:

- Front-End Accuracy – Verify demographics, eligibility, and authorizations.
- Ongoing Training – Keep billing and coding staff up to date on rules and regulations.
- Track KPIs – Monitor denial rates, clean claim rates, and days in A/R.
- Leverage Automation – Use RPA or AI to flag high-risk or incomplete claims.
- Collaborate with Payers – Maintain clear communication to address recurring denial patterns.
The Financial and Operational Impact of Denials
According to the American Hospital Association (AHA), U.S. hospitals spent $19.7 billion in 2022 resolving claims that were wrongly denied. Each appeal costs an estimated $40–$50 and adds extra days to A/R cycles, directly draining revenue.
By contrast, practices that implement structured denial management workflows can reduce A/R days by up to 40% and significantly strengthen their cash flow.
AHA Reports:
- $19.7B spent resolving wrongly denied claims
- $40–$50 cost per appeal
This is why every improvement in denial management directly increases free cash flow and operational stability.
How AI Is Transforming Denial Management
Automation tools such as AI-driven denial prediction and RPA bots have transformed how billing teams handle denials. About 46% of hospitals and health systems now use AI in their RCM and billing operations, according to an AKASA 74% of hospitals implement some form of revenue-cycle automation, which includes robotic process automation (RPA). However, the use of AI for RCM is often limited to specific functions and healthcare operations.
RPA adoption is widespread (74%), while true AI-driven denial prediction is still emerging (~46%)
AI Advantages:
- Predictive Analytics: Identify high-risk claims and prevent their filing.
- Faster Processing: Charge entries, EOBs ,and payer follow-ups are automated, which accelerates the processing.
- Fewer Human Errors: Reduced human errors will lead to minimal errors in data entry that have resulted in claim rejection.
- Real-Time Insights: Trends and performance are monitored through real-time dashboards.
AI is not replacing staff, it is eliminating low-value tasks so teams can focus on revenue-driving work.
Key Industry Benchmarks
CMS and HFMA indicate that the denial practices should aim to keep denial rates under 5% to maintain the financial situation and eliminate the loss of revenues.
| KPI | Target | Description |
| Claim denial rate | ≤ 5% | Measures the frequency of denied claims |
| Net collection rate | ≥ 95% | Revenue collected after contractual adjustments |
| Clean claim rate | 98% | Claims accepted without edits |
| Days in A/R | ≤ 40 days | Average time to collect payment |
| Denial resolution time | ≤ 30 days | Duration to resolve denials |
Why is Outsourcing Denial Management Important
For many practices, managing denials in-house can be time-consuming and resource-heavy. Outsourcing to a medical billing company gives you access to trained RCM experts, advanced tools, and proven workflows.
Key Benefits of Outsourcing:
- Specialized Expertise: Certified billing professionals handle complex payer rules.
- Faster Reimbursements: Dedicated denial management teams shorten follow-up cycles.
- Technology Advantage: Access to automation and analytics without high setup costs.
- Compliance and Security: Adherence to HIPAA and payer-specific requirements.
Outsourcing adds expert oversight without adding payroll burden.
Checklist: Is Your Denial Management Process Working?
- You track denial trends monthly.
- Denials are resubmitted within 30 days.
- Payer-specific patterns are analyzed.
- Denial rate stays below 5%.
- Automation supports claim validation.
- A/R days are monitored regularly.
The Bottom Line
Denial management is about revenue protection; every claim counts. If your denial rate is above 5% or A/R days exceed 40, your practice is already leaking revenue every month.
A structured denial workflow combined with automation and specialized RCM support can recover 20–40% of lost revenue.
Want to Know How Much Revenue You’re Losing and How Much You Can Recover? Contact Dastify Solutions today for a complimentary denial analysis!


